Plasmid Nomenclature in Officinae Bio
A guide to plasmid nomenclature in Officinae Bio based on the Standard European Vector Architecture (SEVA) standard.
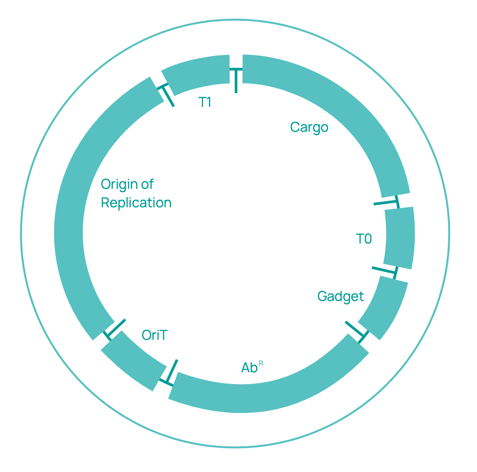
The SEVA format comprises a set of guidelines for physically assembling the three essential components of plasmid vectors - the origin of replication, selection marker, and the business cargo. In addition to the standard layout of constructs, the SEVA format mandates a specific nomenclature for designating each vector. The nomenclature follows a code that is explained in detail below.
All vectors must be designated with the prefix "pSEVA" followed by a four-digit code. The first digit indicates the antibiotic resistance marker, the second indicates the origin of replication, and the third represents the cargo module. In cases where multiple variants of the same cargo type exist, a capital letter is added to the numeral. The fourth digit is reserved for gadgets, which are designated by lowercase Greek letters.
List of SEVA modules and codes
Position 1: Antibiotic Resistance MarkerThis module includes the structural gene for the antibiotic of choice with its own native promoter.
|
|
| Marker | code |
| Ap | 1 |
| K | 2 |
| Cm | 3 |
| Sm/Sp | 4 |
| Tet | 5 |
| Gm | 6 |
| Tmp | 7 |
| Apra | 8 |
| Km_G+ | 2a |
| CG_G+ | 3a |
Position 2: Origin of ReplicationThis module comprises the oriV sequence and the replication proteins |
|
| ORI | Cipher |
| R6K | 1 |
| RK2 | 2 |
| pBBR1 | 3 |
| pRO1600/ColE1 | 4 |
| RSF1010 | 5 |
| p15A | 6 |
| pSC101 | 7 |
| pUC | 8 |
| pBR322-ROP | 9 |
| RK2-int-phiC31 | 2a |
| RK2-SCP2* | 2b |
| pIJ101-RK2 | 2c |
| pSM19035-RK2 | 2d |
| pBBR1-int-phiC31 | 3a |
| pBBR1-SCP2* | 3b |
| pUC-int-phiC31 | 8a |
| pUC-SCP2* | 8b |
| pIJ101-pUC | 8c |
Position 3: CargoThis DNA portion confers functionality to the vectors. |
|||
| Cargo | Code | Cargo | Code |
| Cloning | Multifunction | ||
| MCS | 1 | XylS-Pm —> I-Scel | 8S |
| LacZalpha-pUC19 | 2 | PEM7 —> I-SceI | 13S |
| LacZalpha-pUC19-ISceI | 2S | PEM7 —> GFP | 13G |
| LacZalpha-pUC18 | 3 |
PEM7 —> mCherry |
13R |
| LacZalpha-pUC18-IIs sites up | 3X | PPEM7 —> mTurquoise2 | 13T |
| LacZalpha-pUC18-IIs sites down | 3Y | XylS-Pm —> msfGFP | 8M |
| Promoter - Probe | LacIq-Ptrc —> GFP | 4G | |
| LacZ | 5 | AlkS-PalkB —> msfGFP | 9M |
| LacZ | 5T | ChnR-PchnB —> msfGFP | 11M |
| Lux | 6 | XylS-Pm —> msfGFP-Nt | 8MN |
| GFP | 7 | XylS-Pm —> msfGFP-Ct | 8MC |
| CFP | 7C | T7 —> msfGFP | 25M |
| YFP | 7Y | PEM7 —> PHP | 13P |
| DsRed2 | 7D | Modular Cloning | |
| mCherry | 7R | Golden Standard | 19 |
| msfGFP | 7m | Metagenomics | |
| EcFbFP | 7F | cos-T7-ccdB-T3 | 15 |
| GFP-LVA | 7V | CRISPR | |
| mECFP | 7B | CRISPR array | 16 |
| Expression System | |||
| LacIq-Ptrc | 4 | PLiar_53 | 17 |
| LacIq-Ptac | 4R | PLiar_15 | 17A |
|
LacIq-PT7/LacO
|
4E | PLiar_17 | 17B |
|
LacIq-PT5/LacO
|
4F | PLiar_51 | 17C |
| LacIq-Ptrc standard | 4C | PLiar_53 | 17D |
| XylS-Pm | 8 | PLiar_1 | 17E |
| AlkS-Palk | 9 | RhaRS-Prham | 18 |
| AraC-PBAD | 10 | PD_E20(T5 | 20 |
| ChnR-PchnB | 11 | PLacIq | 21 |
| CprK1-PDB3 | 12 | PR | 21 |
| PEM7 | 13 | PRM | 23 |
| cI857-PL | 14 | PA1/04/03 | 24 |
| T7 | 25 | ||
Position 4: GadgetA gadget is a dispensable DNA sequence that confers a new utility/property to the basic frame of the backbone plasmid. |
|
|
Gadget
|
Code |
|
Hok-sok
|
alpha |
| CEN6-ARS209-URA3 | beta |
Deriving the Nomenclature
| AntiBiotic Marker / Origin of Replications | Cargo | Gadget | |||
| # 1-9 | 9 | Single Modules | 1 -n | Monofunction | -- |
| # >9 | 9A | ||||
| # <9 | 2A | Doubles or Variants | 8 M | Variants or Multifunction | |
| # >9 | 9AB | 8MC | |||
The table provides an outline of the expanded regulations for naming each of the four positions involved in creating a complete SEVA code. The first position indicates the antibiotic resistance, while the second position represents the origin of replication, which is identified by a single numeric code ranging from 1 to 9. If there are any variants or additions to either the antibiotic marker or a second replication origin, a lowercase letter is added next. The third position is for the cargo, which can be either mono-functional (designated by a number from 1 to n) or a variant/multi-functional thereof (designated by a number followed by a capital letter). Finally, the fourth position is reserved for gadgets, which are labeled with lowercase Greek letters ranging from α to ω.
For example, the code pSEVA237M signifies a plasmid for kanamycin (KmR) seletion and has a replication origin of pBBR1, with a mono-functional cargo of promoterless msfGFP reporter. Another example is pSEVA2313R, which indicates a KmR plasmid with a pBBR1 origin of replication and a bi-functional cargo of PEM7–>mCherry. Lastly, pSEVA2a2b8Rα means a KmR plasmid that can be selected in Gram-positive hosts, featuring a double RK2-SCP2* replication origin, a bi-functional cargo of xylS-Pm–> mCherry, and a gadget of hok-sok.